Face Recognition System for Identification
Overview
This project focuses on developing a Face Recognition System for identification, leveraging multiple deep learning models such as Face Recognition, Dlib, Facenet, and VGG-Face. The system is designed to perform image-to-image comparison, real-time webcam recognition, and face enrollment through a user-friendly PyQt5-based GUI. The application integrates with a MySQL database to store and manage face data, making it suitable for security, access control, and identity verification scenarios.
The system supports multiple recognition modes, including image recognition, capture and recognize, and real-time webcam recognition. Additionally, it includes a face enrollment system to add new faces to the database.
Key Features
- Multiple Recognition Models: Supports Face Recognition, Dlib, Facenet, and VGG-Face, allowing users to choose model.
-
Multiple Recognition Modes:
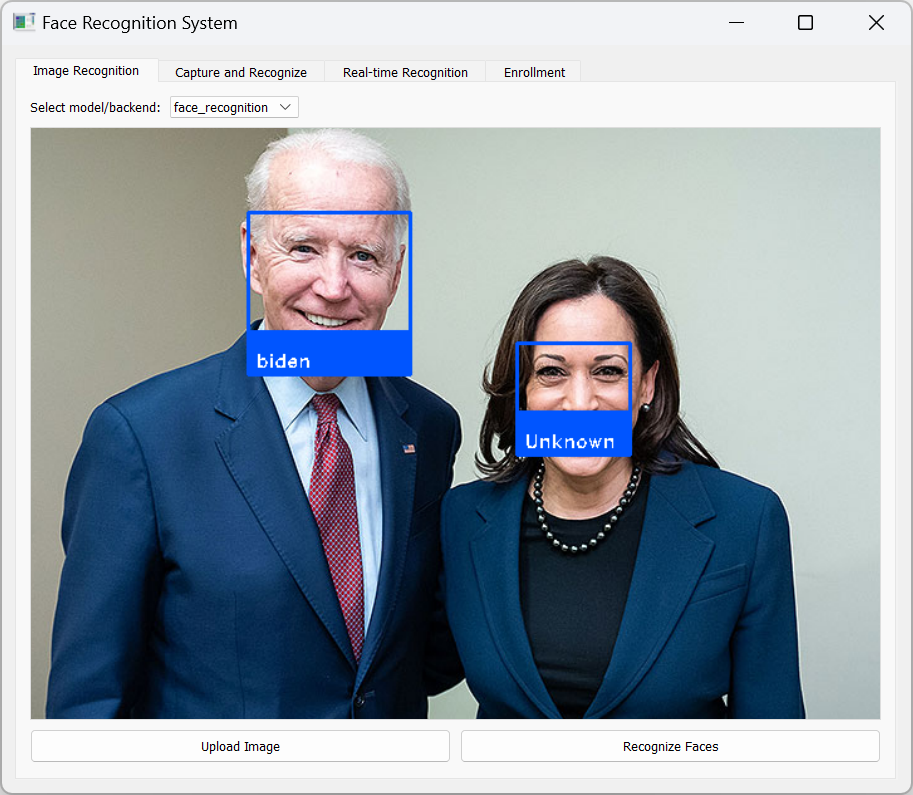
- Image-to-Image Comparison: Identify faces in uploaded images.
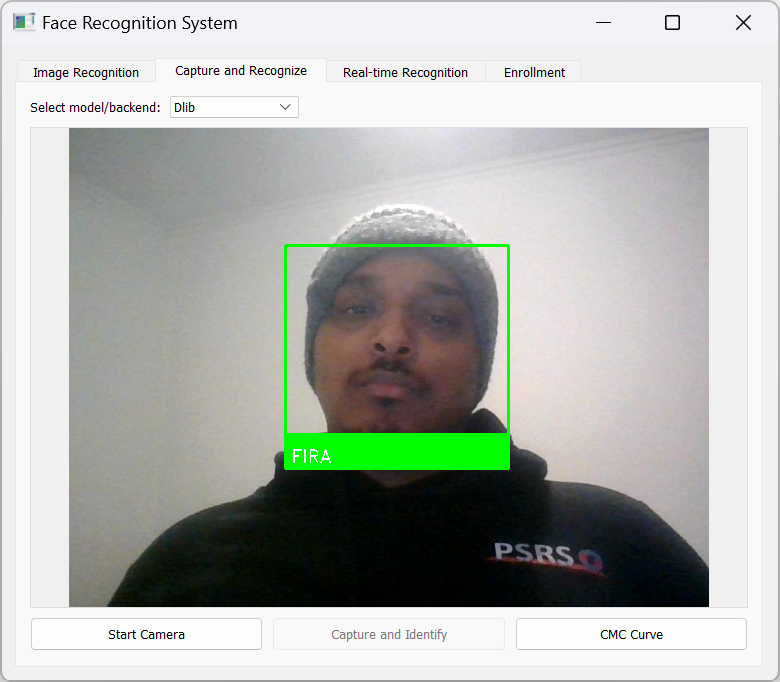
- Capture and Recognize: Capture an image using the webcam and identify faces.
- Real-Time Webcam Recognition: Perform real-time face recognition using live video.
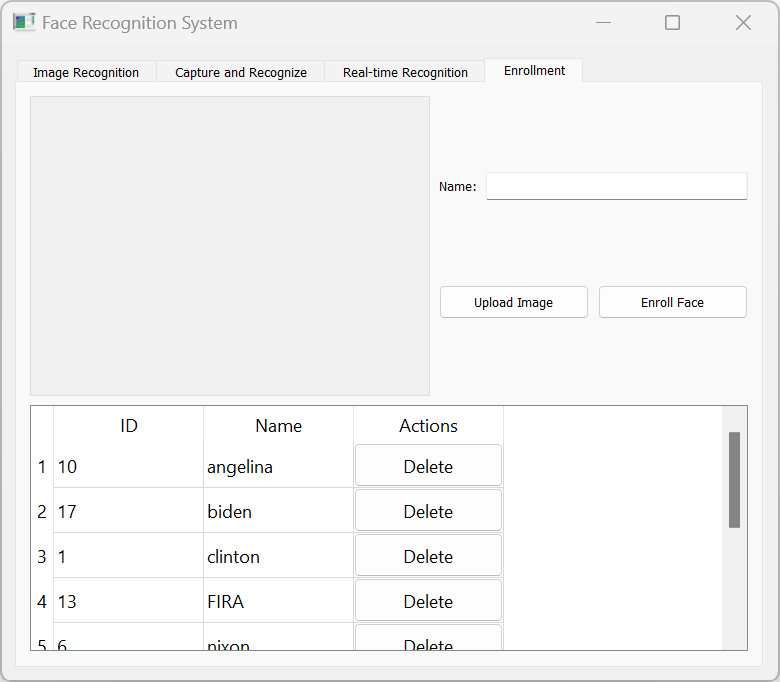
- Face Enrollment System: Add new faces to the database with names and images.
- Database Integration: Uses a MySQL database to securely store and retrieve face data.
- User-Friendly Interface: The PyQt5-based GUI ensures ease of use, with tab-based navigation and intuitive controls.
Technical Details
The system was developed using a modular architecture, ensuring flexibility and scalability. Key technical components include:
- Programming Language: Python
- GUI Framework: PyQt5
- Deep Learning Models: Face Recognition, Dlib, Facenet, VGG-Face
- Key Libraries: OpenCV (for image processing), TensorFlow (for deep learning), NumPy (for numerical computations), MySQL Connector (for database integration)
-
Architecture: The system is divided into four main components:
- User Interface: Handles user interactions and displays results.
- Model Management: Manages the loading and switching of deep learning models.
- Image Processing: Preprocesses input images and performs face detection and recognition.
- Database Management: Stores and retrieves face data from a MySQL database.
Face Detection and Recognition Process
-
Face Detection: Uses OpenCV’s Haar Cascades and deep learning-based detectors from the
face_recognitionandDeepFacelibraries. - Feature Extraction: Converts detected faces into numerical embeddings (feature vectors) using pre-trained models.
- Face Recognition: Compares embeddings with known faces in the database using Euclidean distance and cosine similarity.
Database Interaction
The system integrates with a MySQL database to manage face data:
- Storing Face Data: Saves face images (binary data) and names during enrollment.
- Retrieving Known Faces: Retrieves and processes known faces for recognition tasks.
Performance and Applicability
The system’s performance depends on the selected model, computational efficiency, and hardware. Key performance metrics include:
- Speed and Efficiency: Real-time processing requires a decent CPU or GPU, and larger databases increase matching time.
- CMC Curve: Evaluates system performance using Cumulative Match Characteristic curves.
Optimization Challenges and Suggestions
- Challenges: Real-time processing is computationally expensive due to repeated steps per frame.
-
Suggestions:
- Precompute embeddings during enrollment.
- Use efficient data structures (e.g., NumPy arrays or FAISS).
- Implement batch processing and hardware acceleration.
Demo
Future Improvements
While the system performs well in its current state, there are several areas for future enhancement:
- Optimization: Precompute embeddings and use lightweight models for faster processing.
- Scalability: Implement support for larger databases and cloud-based services.
- User Interface: Enhance the GUI with additional features, such as performance metrics and advanced settings.
