Face Recognition System for Biometric Verification
Overview
This project focuses on developing a Face Recognition System for biometric verification, leveraging state-of-the-art deep learning models such as VGG19 and Xception. The system is designed to perform both image-to-image comparison and real-time face recognition through a webcam feed. Built with a user-friendly PyQt5-based GUI, the application provides an intuitive interface for users to interact with the system, making it suitable for both technical and non-technical audiences.
The system was developed using the Labeled Faces in the Wild (LFW) dataset, a widely recognized benchmark for face verification tasks.
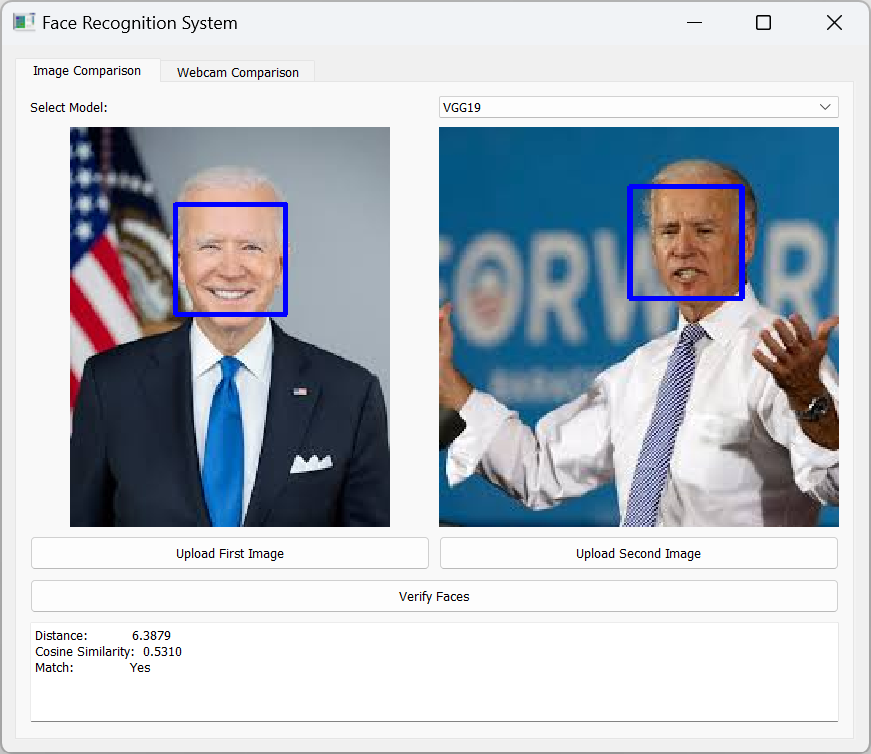
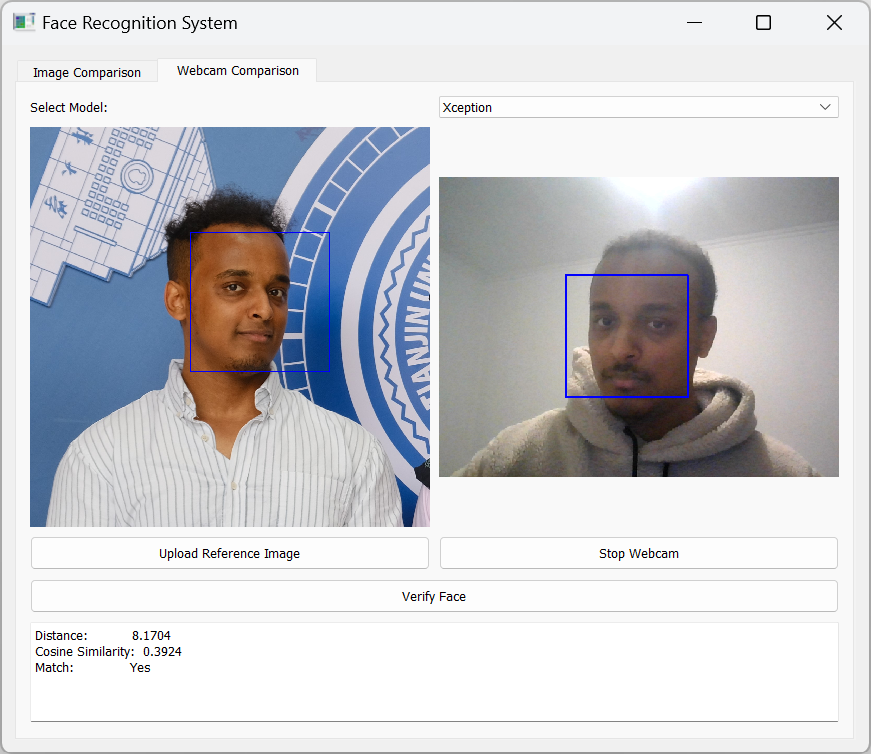
Key Features
The face recognition system offers several advanced features to ensure reliable and efficient biometric verification:
- Multi-Model Support: The system integrates multiple deep learning architectures, including VGG19, Xception, and ResNet, allowing users to choose the most suitable model for their specific use case.
- Real-Time Face Verification: The system can process live webcam feeds to perform real-time face recognition, making it ideal for applications requiring immediate verification.
- Image-to-Image Comparison: Users can compare two images to determine if they belong to the same individual, with detailed similarity scores provided for each comparison.
- User-Friendly Interface: The PyQt5-based GUI ensures ease of use, with clear navigation and intuitive controls for both image and webcam-based verification.
- Detailed Similarity Scoring: The system provides a comprehensive similarity score for each comparison, enabling users to make informed decisions based on the confidence level of the match.
Technical Details
The system was developed using a modular architecture, ensuring flexibility and scalability. Key technical components include:
- Programming Language: Python
- GUI Framework: PyQt5
- Deep Learning Models: VGG19, Xception, ResNet
- Key Libraries: OpenCV (for image processing), TensorFlow (for deep learning), NumPy (for numerical computations)
-
Architecture: The system is divided into three main components:
- User Interface: Handles user interactions and displays results.
- Model Management: Manages the loading and switching of deep learning models.
Dataset and Preprocessing
The system was trained and evaluated on the Labeled Faces in the Wild (LFW) dataset, which consists of 13,233 images of 5,749 unique individuals. For this project, a subset of 2,370 images representing 46 individuals was used, with 1,896 images for training and 474 images for validation. The dataset was preprocessed using resizing, random cropping, flipping, brightness adjustments, and contrast adjustments to enhance model robustness.
Model Training
The VGG19 and Xception models were trained using the Adam optimizer and categorical cross-entropy loss for 10 epochs. Training progress was monitored using validation loss, and the models were fine-tuned to achieve optimal performance.
Performance Metrics
The system’s performance was evaluated using the following metrics:
- False Acceptance Rate (FAR): Measures the likelihood of incorrectly accepting an imposter.
- False Rejection Rate (FRR): Measures the likelihood of incorrectly rejecting a genuine user.
- Equal Error Rate (EER): The point where FAR and FRR are equal, representing a balance between security and usability.
- Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve: Visualizes the trade-off between FAR and FRR across different thresholds.
- Area Under the Curve (AUC): Indicates the model’s ability to distinguish between genuine and imposter pairs.
Results:
- VGG19: Achieved an EER of 0.7320 and an AUC of 0.1953.
- Xception: Achieved an EER of 0.7920 and an AUC of 0.1351.
VGG19 demonstrated superior performance compared to Xception, with a lower EER and higher AUC, indicating better discrimination between genuine and imposter pairs.
Demo
Future Improvements
While the system performs well in its current state, there are several areas for future enhancement:
- Integration with Databases: Adding support for large-scale face databases to enable identity verification against a predefined set of individuals.
- Mobile Compatibility: Developing a mobile-friendly version of the system to expand its applicability to smartphones and tablets.
- Enhanced Anti-Spoofing: Incorporating advanced techniques, such as 3D face recognition or liveness detection, to further improve security.
